Skin Biopsy Techniques
If you've ever had a suspicious skin lesion, your healthcare provider may have recommended a biopsy. This procedure is essential for diagnosing various skin conditions, including cancers and inflammatory diseases. Understanding the different types of skin biopsies can help demystify the process and prepare you for what to expect.
🔬 What Is a Skin Biopsy?
A skin biopsy involves removing a small sample of skin tissue to examine under a microscope. It's typically performed under local anesthesia in a clinic or dermatology office. The choice of biopsy technique depends on factors like the lesion's size, depth, location, and the suspected diagnosis.
🧪 Types of Skin Biopsies
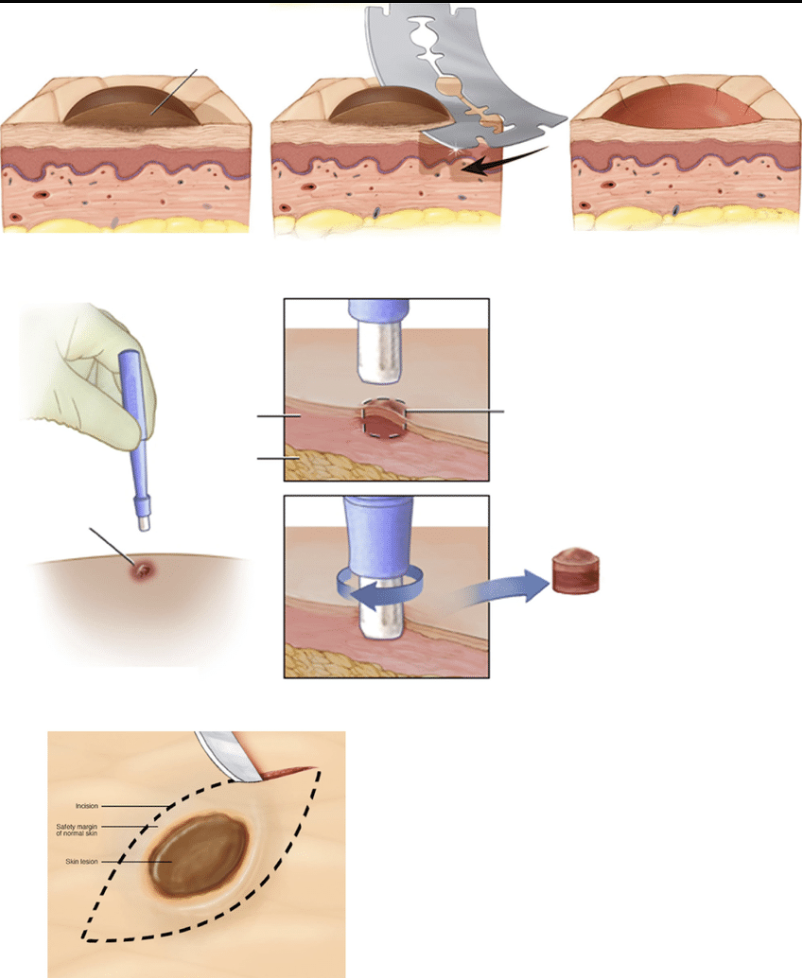
1. Shave Biopsy
A shave biopsy removes the top layers of the skin using a scalpel or razor blade. It's commonly used for superficial lesions like basal cell carcinoma or actinic keratosis. This method doesn't require stitches and usually heals within a few weeks. However, it may not be suitable for deeper lesions, as it doesn't provide a full-thickness skin sample.
2. Punch Biopsy
This technique uses a circular blade to remove a cylindrical piece of skin, including the epidermis, dermis, and superficial fat. Punch biopsies are ideal for diagnosing inflammatory skin conditions and small lesions. Depending on the size, stitches may be needed to close the wound.
3. Incisional Biopsy
An incisional biopsy involves removing a portion of a larger lesion using a scalpel. It's typically used when the lesion is too large to remove entirely or is located in a sensitive area. This method helps in diagnosing conditions like melanoma, where assessing the depth of invasion is crucial.
4. Excisional Biopsy
An excisional biopsy entails removing the entire lesion along with a margin of normal skin. It's the preferred method when melanoma is suspected, as it allows for complete assessment of the lesion's depth and margins. Stitches are required, and the procedure may leave a scar.
🩺 Choosing the Right Biopsy
The selection of a biopsy technique depends on several factors:
-
Lesion Characteristics: Size, depth, and location.
-
Suspected Diagnosis: Superficial lesions may require a shave biopsy, while deeper or pigmented lesions might necessitate a punch or excisional biopsy.
-
Cosmetic Considerations: In cosmetically sensitive areas, less invasive methods may be preferred.
It's essential to discuss the options with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate approach for your specific situation.
🧼 Aftercare and Healing
Post-biopsy care is vital to prevent infection and promote healing:
-
Keep the Area Clean: Follow your provider's instructions on cleaning the wound.
-
Monitor for Signs of Infection: Redness, swelling, or discharge should be reported.
-
Stitch Removal: If stitches are used, they'll typically be removed within 5-14 days, depending on the biopsy site.
Healing times vary based on the biopsy type and individual factors but generally range from one to three weeks.
📊 Final Thoughts
Skin biopsies are invaluable tools in dermatology, aiding in the accurate diagnosis and management of various skin conditions. Understanding the different types can alleviate anxiety and help you make informed decisions about your skin health. Always consult with your healthcare provider to choose the most suitable biopsy method for your needs.
For a visual explanation of these biopsy techniques, you can watch my detailed video here: Understanding Skin Biopsies.
Share this post on:
Copyright © 2024 Dr Finbars' Skin Clinic All rights reserved.